Pulse-number discrimination by Cope's gray treefrog (Hyla chrysoscelis) in modulated and unmodulated noise
Study of treefrogs' reactions to sounds
By Alejandro Vélez, Betsy Jo Linehan-Skillings, Yuwen Gu, Yuting Sun, and Mark A. Bee in Research Consulting
October 3, 2013
Alejandro Vélez, Linehan-Skillings, B. J., Gu, Y., Sun, Y., & Bee, M. A. (2013). Pulse-number discrimination by cope’s gray treefrog (hyla chrysoscelis) in modulated and unmodulated noise. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 134(4), 3079–3089.
Abstract
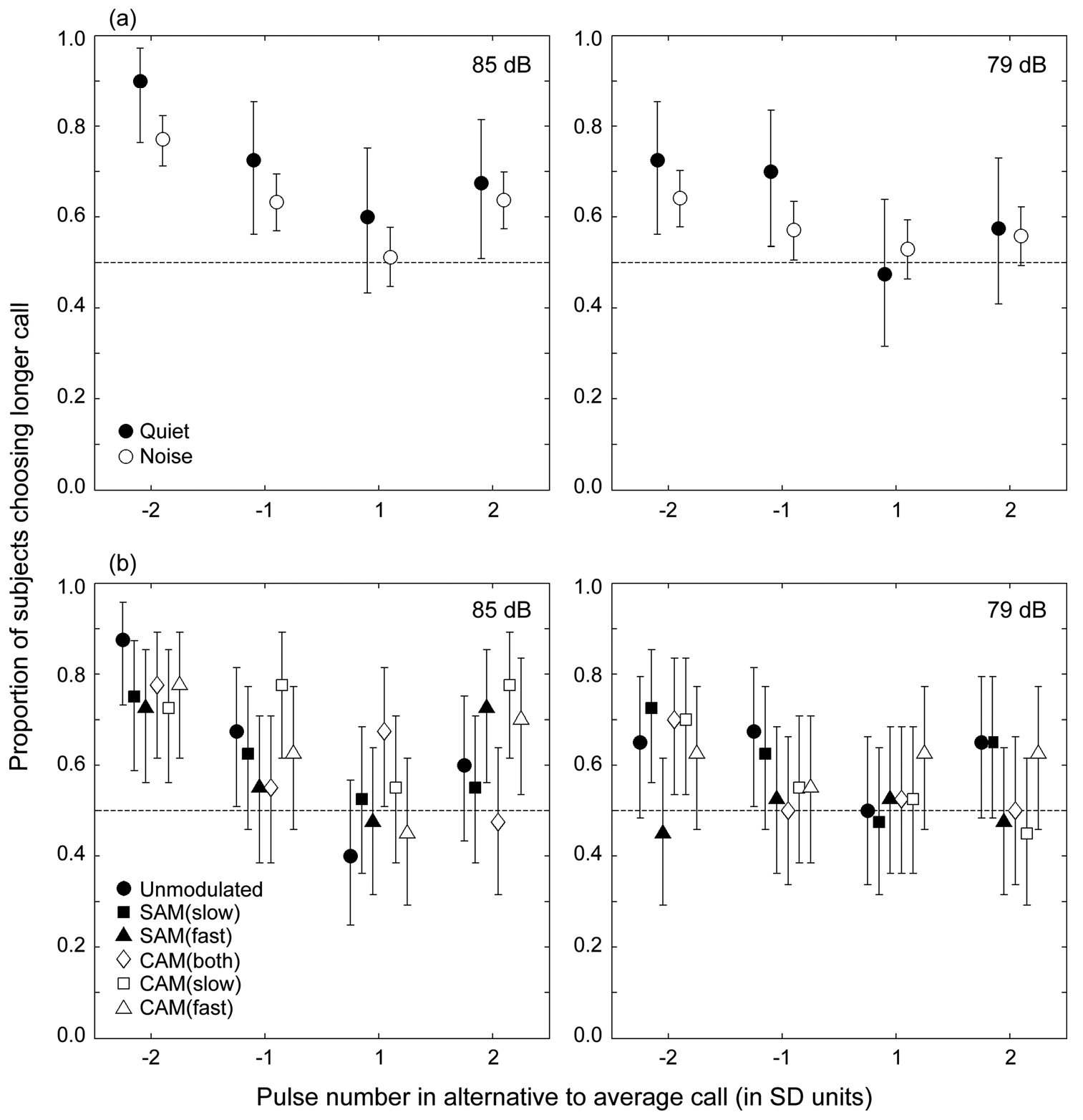
In Cope’s gray treefrog (Hyla chrysoscelis), thresholds for recognizing conspecific calls are lower in temporally modulated noise backgrounds compared with unmodulated noise. The effect of modulated noise on discrimination among different conspecific calls is unknown. In quiet, females prefer calls with relatively more pulses. This study tested the hypotheses that noise impairs selectivity for longer calls and that processes akin to dip listening in modulated noise can ameliorate this impairment. In two-stimulus choice tests, female subjects were allowed to choose between an average-length call and a shorter or longer alternative. Tests were replicated at two signal levels in quiet and in the presence of chorus-shaped noise that was unmodulated, modulated by a sinusoid, or modulated by envelopes resembling natural choruses. When subjects showed a preference, it was always for the relatively longer call. Noise reduced preferences for longer calls, but the magnitude of this reduction was unrelated to whether the noise envelope was modulated or unmodulated. Together, the results are inconsistent with the hypothesis that dip listening improves a female gray treefrog’s ability to select longer calls in modulated compared with unmodulated noise.
- Posted on:
- October 3, 2013
- Length:
- 2 minute read, 221 words
- Categories:
- Research Consulting
- Tags:
- GLMM Application
- See Also: